Some Lectures Notes
Part 0.Number Representation
Lec2
Numbers' Representation
- Unsigned Numbers 🚀

-
Sign and Magnitude(to represent negative numbers) 🙅
-
We define the first bits to be sign! 0 is positive and 1 is negative (rest of bits are numerical value).This way we called Sign and Magnitude(原码)
-
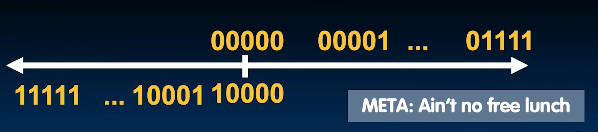
Ain't no free lunch!So we lose one bit to represent sign.
-
But now,there are some problems.When the bits grow up, at first we will get positive but then we get nagitive.Werrid.
-
-
Shortcomings of Sign and Magnitude
-
Arithmetic circuit complicated.
- Because you need to deal with the fact that it's positive or negative.
-
Two zeros
and
-
Incrementing "binary odometer", sometimes increases values, and sometimes decreases!
-
-
One's Complement 🙅
-
Flipping all the bits when number is negative.
- e.g.
(7 in decimal is 0111 in binary), (in 4-bit two's complement representation)
- e.g.
-

-
Shortcomings of One's Complement
-
Arithmetic still somewhat complicated
-
Still two zeros
-
-
Two's Complement 🚀
-
Interpret the most significant digit of a binary number as a negative weight
-
Some tips
- All 1 is always represent negative 1 in this two's complement number
-
non-negatives and negatives, and one zero (no overlap now)
-
-
Bias Encoding:
(bias = ) 🚀 -
unsigned + bias (e.g.,
to - -> to ) -
Bias for
bits chosen as -
Now we have a beautiful odometer! Starting with the smallest negative number. And it can handle all situations correctly.
-
Numeral vs Number vs Digit
The conception of Number is a number, but the representation of the Number is a numeral.
e.g.
5is a number, but we can represent it in may different ways, such as101in binary, that101is the binary numbral.
Digits are used for represent a numeral.Digits made from 0-9.
e.g. The numeral
153is composed of three digits:1,5, and3; the numeral9is made up of a single digit,9
Part 1.C Program
Lec3
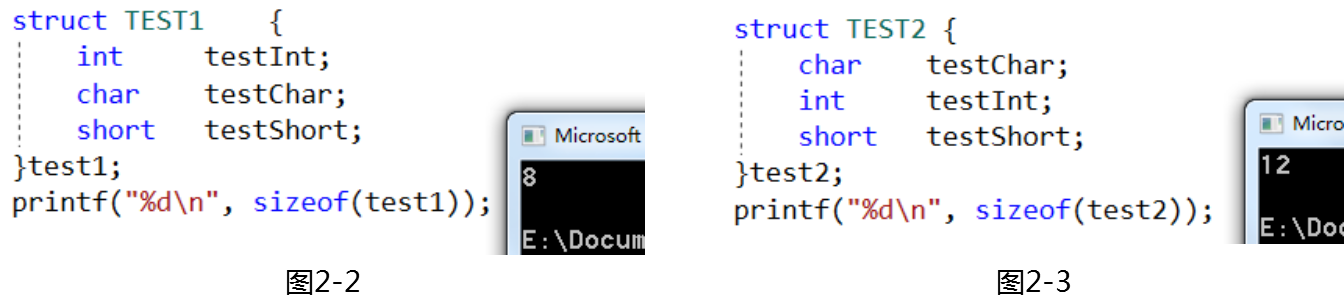
Encourage to use the precise bit width int.Beacause the return value of command sizeof(int) is depends on the target processor(16,32 or 64).
Lec4
Notes of Undefined Behavior
-
Undefined Behavior
In my thinking, it point the bugs that appear when the environment changes.
-
HeisenBugs
Random bug which hard to repeat or track
Cf. Bohrbug is the repeatable bug.
Pointer Syntax
Thinking about following sentence`s function.
int *p;
//Tells compiler that variable p is address of an int.But now, *p doesn`t have any argue, so it is a garbage.
p = &y;
//Tells compiler to assign address of y to p.& called the "address operator" in the context.
z = *p;
//Tells compiler to assign value at address in p to z.* called the "dereference operator" in this context
*z = p;
//Tells compiler to assign value of p to value at address in z.
initlizing variable correcttly!
Some instance
void addOne (int x) {
x = x + 1;
}
int y = 3;
addOne(y);
- Thinking about what the current value of
y?
You may say y is 4.But the answer is still 3.Beacuase this function(subroutine) just pass the value of y and return void, the value in address of y acutally never been changed.
- Try to use the
Pointerto solve this problem.
void addOne(int *p) {
*p = *p + 1;
}
int y = 3;
addOne(&y);
The Advantage Of Pointer
- Why use pointers.
If we want to pass a large struct or array, it's easier / faster / etc. to pass a pointer than the whole thin
When we proccess a large data, we dont need to copy a mount data to process.We just throw a link to the subroutine and say, hey , there is the data you need to process , just get it and do your work.
Pointers and Structures
First of all, we have a struct.
typedef structure {
int x;
int y;
} Point;
Point p1;
Point p2;
Point *paddr;
paddr = &p2;
- Dot Notation
int h = p1.x;
p2.y = p1.y;
- Arrow Notation
int h = paddr->x;//get value "x" of the struct pointed by address of paddr.
int h = (*paddr).x;//"*paddr" is point a struct.
- We also can use "="
p1 = p2;//Metion, now the p1 and p2 have the same value, in other words, there are two copy data, p1 and p2 dont share a same data.
Alignment
Notice, the following image is about byte alignment, but it can help you to understand Word Alignment
In order to improves CPU data access efficiency
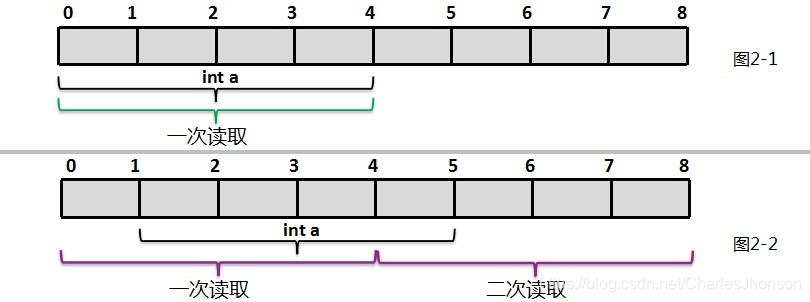
Save storage space
Arrays
An array variable is a pointer to the first element.
-
ar[0] is the same as
*ar. -
ar[2] is the same as
*(ar+2).
Scope
char *foo() {
char string[32];
...;
return string;
}
is incorrect.
Maybe you have some questions, why the return type is "char *" ?Acutally the string is a character pointer to point the first element of a character arrays.
Segmentation faults and bus errors
-
Segmentation faults:You're reading and writing to memory you don't have access to.
-
bus erros:Your alignment is wrong.
Function Pointer
e.g.
#include <stdio.h>
int x10(int), x2(int);
void mutate_map(int [], int n, int(*)(int));
int x2 (int n) {
return 2*n;
}
int x10 (int n) {
return 10*n;
}
void mutate_map (int A[], int n, int(*fp)(int)) {
....
}
int(*fp)(int) The first int is the return type, the second one is pass type.
Lec5
Dynamic Memory Allocation
Using the malloc()function.
malloc() takes in the number of bytes you want and returns a pointer as a void * (breacause malloc dont know what type is we want)to a uninitialized space.So, we need to cast it when using.
- prt = (int ) malloc (nsizeof(int));
Once malloc() is called, the memory location contains garbage, so don't ust it until you've set its value.
Don't forget to free it.
- free(ptr)
Weird value of &a
int a[4];
*a = 3;
printf("*a:%u, a:%u, &a:%u", *a, a, &a);
The way of using pointer
-
Give the pointee(the object pointed by pointer) to the pointer when you set up it.
-
Pointer dereferncing starts at the pointer and follows its arrow over to access its pointee.(only works if there is a pointee)
-
Pointer assignment take two pointer to the same pointee.
Normal C Memory Management
-
C has 3 pools of memory
-
Static storage
-
The Stack
-
The Heap
-
-
A program's addreess space contains 4 regions;
-
stack: local variables, grows downward
-
heap: space requested for pointers via
malloc(); resize dynamically, grows upward -
static data: variable declared outside main, does not grow or shrink
-
code: loaded when program starts, does not change
-

So when we need to assign a huge space, we have two way to got it, first is like "array way" e.g. I need a 10 trillion integers, if we don't have the enough space, the program whill crash, but we use the other way malloc() to assign, if we don't have the space, malloc() wil return NULL, So you can now have code that is resilient to memory failure if you used malloc() versus using arrays.
But the array way is faster.And array way can get a continuous space(
malloc()will search free space firstly, if memory space have many uncontinuous slivers, it will be really slow
-
The implementation of
malloc()-
At previous, we know that
malloc()will get fragmentary space, So , it mean that malloc will search the free list first, if there are not enough space,malloc()will return NULL) -
We also know when we call a function, the stack will grows and
malloc()also is a function , so ,when we callmalloc()the Heap and Stack are both affected
-
-
Three ways to find free space when give a request:
-
First fit
-
Next fit
-
Best fit
-
Bad Memory
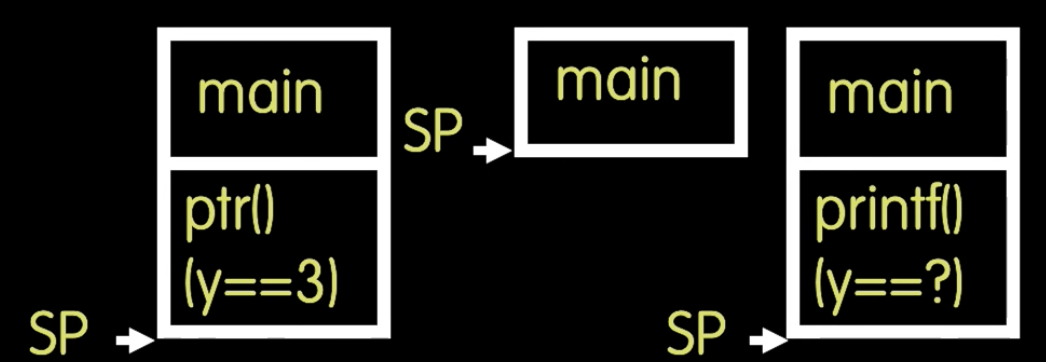
- A simple demo of return pointer into the stack
int *ptr() {
int y;
y = 3;
return &y;
}
main() {
int *stackAddr, content;
stackAddr = ptr();//because the "prt()" is a function call, so when it return, the stack pointer will move upward(relase the stack frame), and "ptr()" return an address of y(address content "3") which exist in the stack frame has just been relased
content = *stackAddr;//stackAddr still points to the address where the "3" was previously stored
printf("%d", content);//"printf()" is a function two, it will clobbers the address where is used to store "3"
content = *stackAddr;
}
-
Once we've freed something, we had no access to it anymore
-
ReallocCan Move DataWhen you do this
struct foo *f = malloc(sizeof(struct foo) * 10);
struct foo *g = f;
...
f = realloc(sizeof(struct foo) * 20);//"g" won't move with f.Result is "g" may now point to invalid memory
- Freeing the Wrong Stuff
struct foo *f = malloc(sizeof(struct foo) * 10);
...
f++;
...
free(f);
-
Double-Free
-
Losing the initial pointer!(Memory Leak)
-
e.g.
f = malloc(...); f++;(this f pointer is moved,i can't free(f),because f is not head anymore) -
use malloc but not use free
-
-
Valgrind
Lec6
intro
What can we represent in
-
things! -
Unsigned integers:
to
-
Signed Integers (Two's Complement)
to
Using the Fixed Point Number to intro Flating Point number
Why do we need Floating Point?
Because we need the support of very big numbers or very small numbers.
e.g.
Floating Point Representation
- IEEE 演示网站

Exponent use two's complement
- There is always a leading 1 unless all 0.

-
overflow&underflow
-
overflow is tends to infinity
-
underflow is tends to 0.When we calculate, some numbers may past the underflow, than we think it is 0
-
-
The way to solve Two 0 problem
-
0 has no leading 1.The exponent value is 0 when the bits were all 0
-
But we have sign bits, so that we have two 0(positive and nagitive)
-
-
Make the smallest one to be in the negative.(When we have all 0 bits pattern ,It represents the smallest number)
-
We use the Biased Notation,where bias is number subtracted to get real number
- IEEE 754 uses bias of 127 for single precision.Because The Exponent have 8 bits
-
Now we have all 0 bits pattern to represent -127.The bigger the exponent, the bigger the number.(like bias encoding we mention in lec2)
-

-
Special Numbers
- In FP, divide by 0 should produce \pm\infin, not overflow.(The decimal part is all 0, the exponent part is all 1, and the sign bit represents positive and negative)
Here are some numbers we don't use so far.We will use it instead of threw those bits away.

-
Not a Number(NaN)
-
Meaningless numbers like
, -
The exponent is all 1 and the decimal is not 0.(Exponent 255, Significand nonzero)
- We find that if that is the rule of NaN, we have a lot of numbers to use,23bits!So we use it to store different error messages.
-
-
Denorm Numbers
- The smallest positive number with meaning is a decimal with all 0s and an exponent of 1 (-126), i.e.,
. The second smallest is a decimal of (i.e., ). Using Denorm Number to fill the gap between it and 0.
- The smallest positive number with meaning is a decimal with all 0s and an exponent of 1 (-126), i.e.,
-
If the exponent is all 0 and the decimal is nonzero, then the exponent is actually -127. But we define that there are no leading 1s, implicit exponent = -126.
-
Smallest representable positive number:
(i.e., or Exponential form is ). -
Second smallest representable positive number:
, and then is . -
Every time the exponent increases, double the size of stride.
-


Tips
If you ever want to pull updated starter code, you'd execute the following command:
git pull starter main
